<http>
Description: command for conducting http queries
Required parameters for HTTP command:
- comment
- alias - unique name of the API you configured in your
integration.xmlfile
Optional parameters:
- condition - condition according to which this test step will or won't be executed
- threshold - parameter, where the maximum execution time of the command is defined (milliseconds), if the execution time is exceeded, the step will be defined as failed
Available HTTP methods:
- GET
- POST
- PUT
- DELETE
- PATCH
- HEAD
- OPTIONS
- TRACE
Parameters for HTTP methods:
endpoint - endpoint for your query
response
- code - expected response code
- file - file with expected result for particular query
header
- name - name of header
- data - data which header has to contain
body (for those methods, which require body)
from
- file - json file that contains body of your request. This file must be named "request_N.json", where N is number of your test step
param
- name - name of parameter
- data - data which parameter has to contain
multipart
- file
- name - key
- fileName - value
- contentType
- file
raw - you can put your request body just as raw in scenario without file
- response
- header
- body/param
Steps
- In an already created scenario or in a new one created:
- Make sure that
WEBcommand is closed or absent
- Open
httpcommand, fill in the comment and alias
- Select a request method
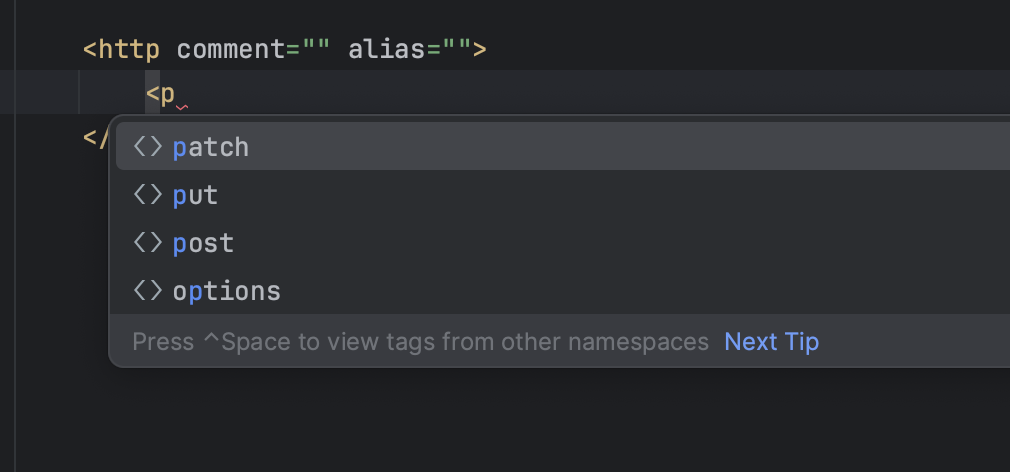
- Indicate
endpointandresponse code
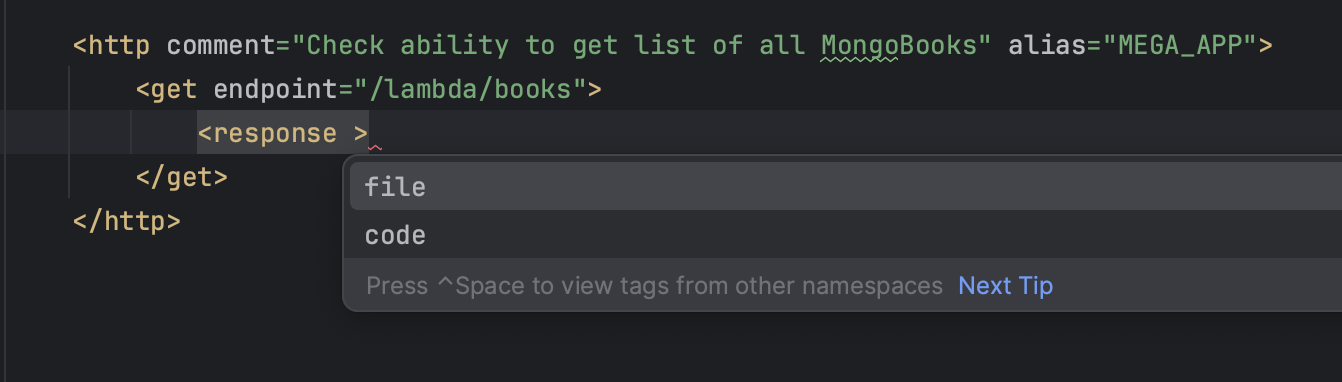
- Create an empty
expected_file.jsonin the scenario folder
- Indicate expected_file.json in
httprequest
- The number of expected_file depends on the number of the tested scenario’s step
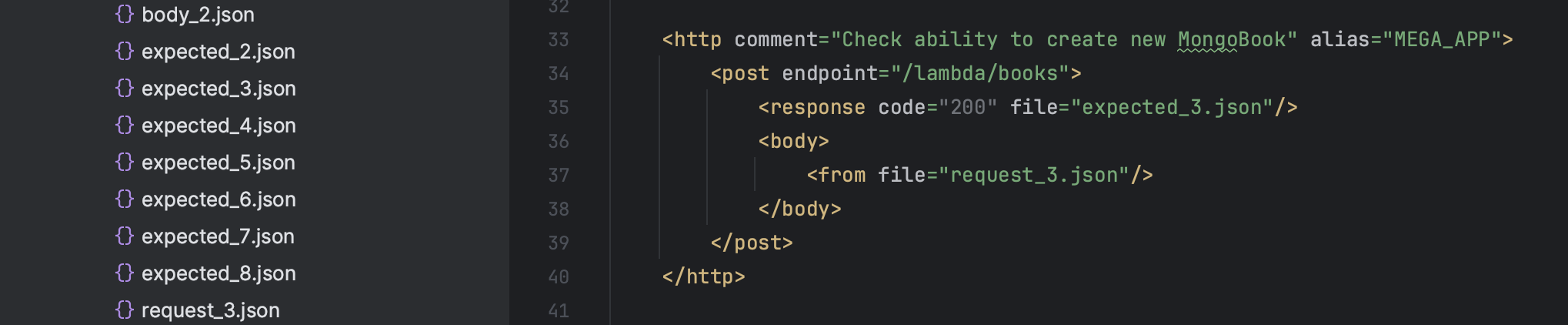
- Select a transfer type of the body of the request
- Open
<body>tag
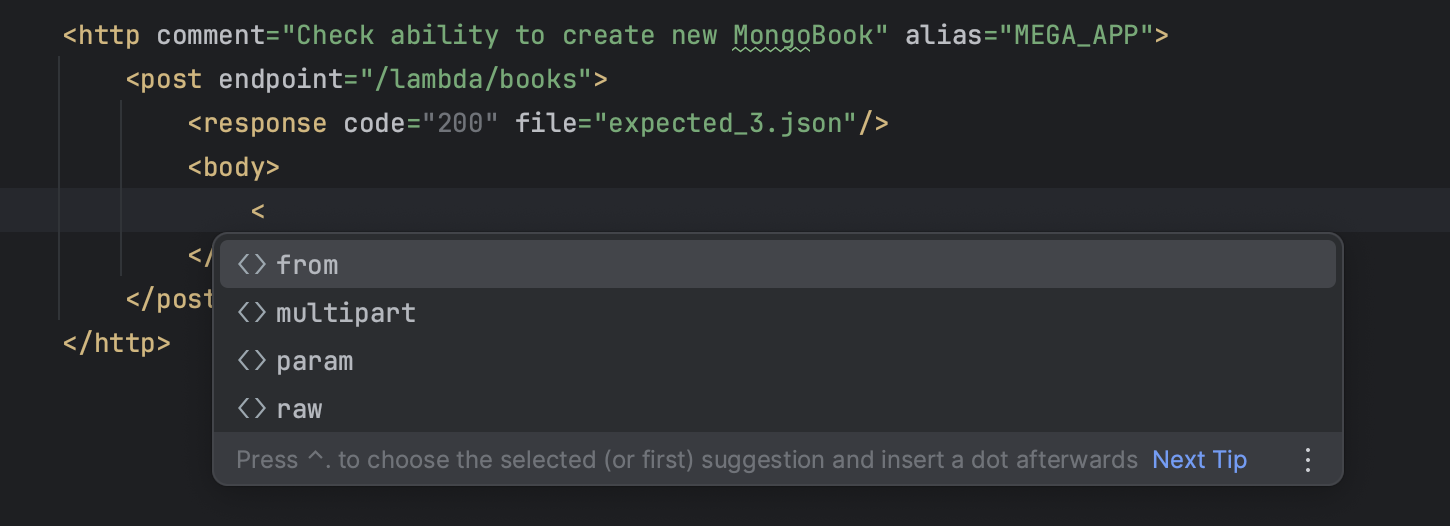
- An example of transferring the body of the request using
<from>file parameter
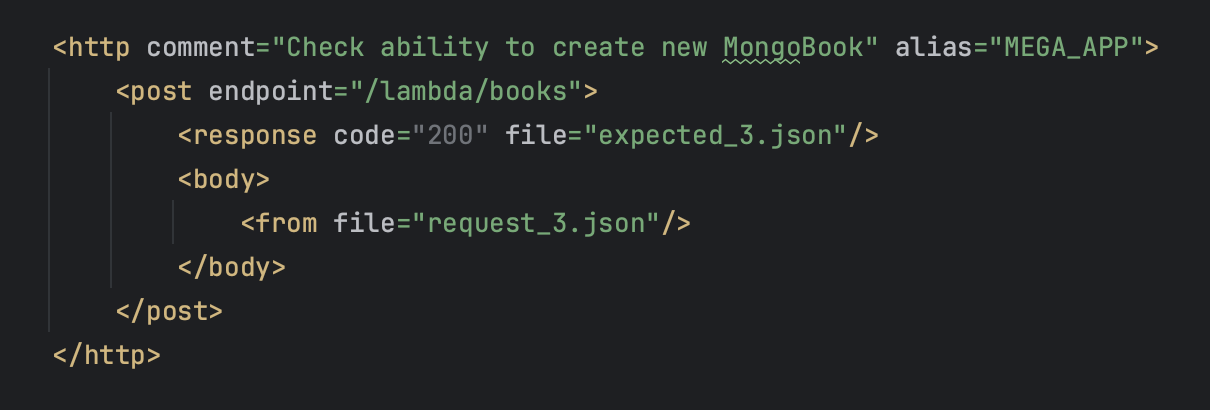
- Create
request_file.jsonto transfer the body of the request (in the scenario folder)
- Put the body of the request into created
request_file.json
- Set a name request_file.json - inside of
<from file=""/>
YouTube Instructions API
Instructions for working with the
APItest scenario
'To start, click on the running line'
VAR
The Usage of Variations makes your API tests more efficient and flexible. Therefore we recommend you checking more information regarding it here
Structure HTTP
The HTTP request structure has all the basic features of API testing tools.
HTTP in a test scenario
<http comment="Add product with id = 1 to card" alias="ALIAS"> <post endpoint="/api/v1/cart"> <response code="201" file="expected_1.json"/> <header name="Authorization" data="Bearer {{token}}"/> <body> <from file="request_11.json"/> </body> </post></http><mysql comment="Check successfully added new book to cart" alias="ALIAS" file="expected_2.json"> <query> SELECT SHP_CART_ID, SHP_CART_CODE FROM SHOPPING_CART </query></mysql><var comment="Create var for param 'shopping cart code'" name="code"> <path value="$.[0].content.[0].SHP_CART_CODE"/></var><http comment="Get successfully adding product to cart" alias="ALIAS"> <get endpoint="/api/v1/cart/{{code}}"> <response code="200" file="expected_4.json"/> </get></http>Request file
{ "attributes": [ { "id": 1 } ], "product": "TB12345", "promoCode": 1, "quantity": 1}Expected Result
{ "body": null, "errors": { "code": [ "Forbidden" ], "message": [ "Access is denied" ] }, "debugInfo": { "requestId": "p(any)", "stackTrace": null }}Comparison
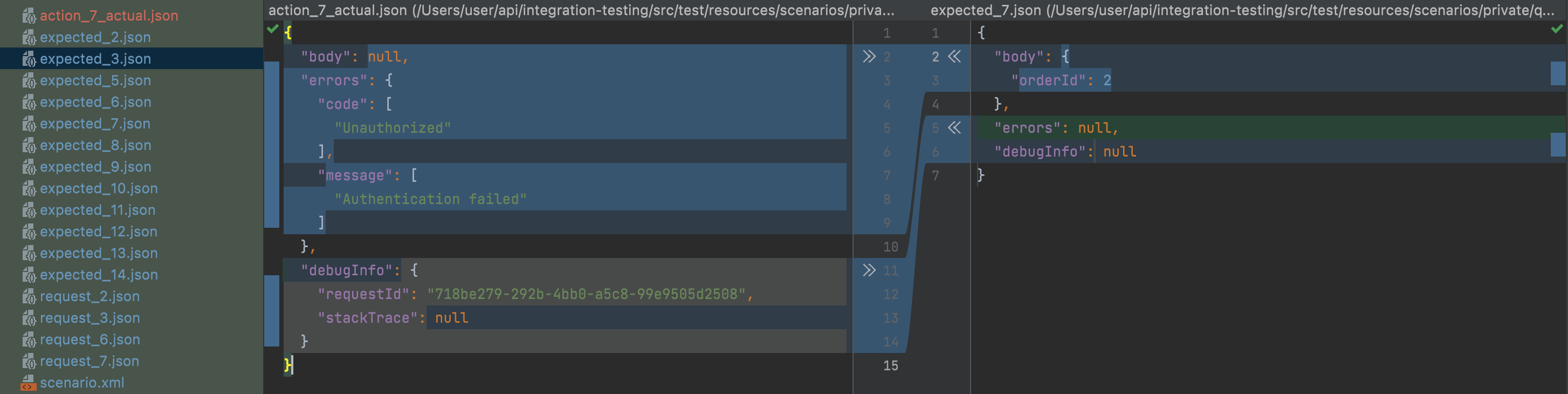
After executing each HTTP request, comparison generates an actual_file which contains the API response in json format with the response code and data.
actual_fileis generated in order for QA-specialist to understand how the system reacted to this check right away. If QA is satisfied with the actual result, then all the data from actual_file, QA transfers to a file calledexpected_file( which is in the http-request structure as the expected result of the test, to pass this test successfully.
HTTP in Testlum allows you to perform smoke testing (and make sure that nothing important is broken), conduct unit and integration testing, run the same tests with various sets of input data, or quickly perform any supporting actions to create test data and situations.
Merge test (WEB/API)
Testlum provides you with ability to conduct different types of testing within one scenario. So that you can easily increase efficiency and coverage level of your tests.
Here is an example of merge test scenario with WEB and API test steps within one scenario