About Testlum
Getting Started
UI Testing
Api Testing
Database Testing
Services Testing
Additional Materials
Title
Message
Create new category
What is the title of your new category?
Edit page index title
What is the title of the page index?
Edit category
What is the new title of your category?
Edit link
What is the new title and URL of your link?
Logs
Copy Markdown
Open in ChatGPT
Open in Claude
Testlum has informative and easy to read logs.
Each tag has a unique display structure in the logs, due to the individual approach and visualization of tags in the logs.
Uniqueness of logs:
- Ease of perception
- Table structure
- Step by step analysis of the execution of each step of the scenario
- Detailed analysis of the execution of each tag
- Informative output of exceptions
- Displaying the overall result of passing scenarios
WEB Log's Structure
An example of tags display:
<click>
<wait>
<input>
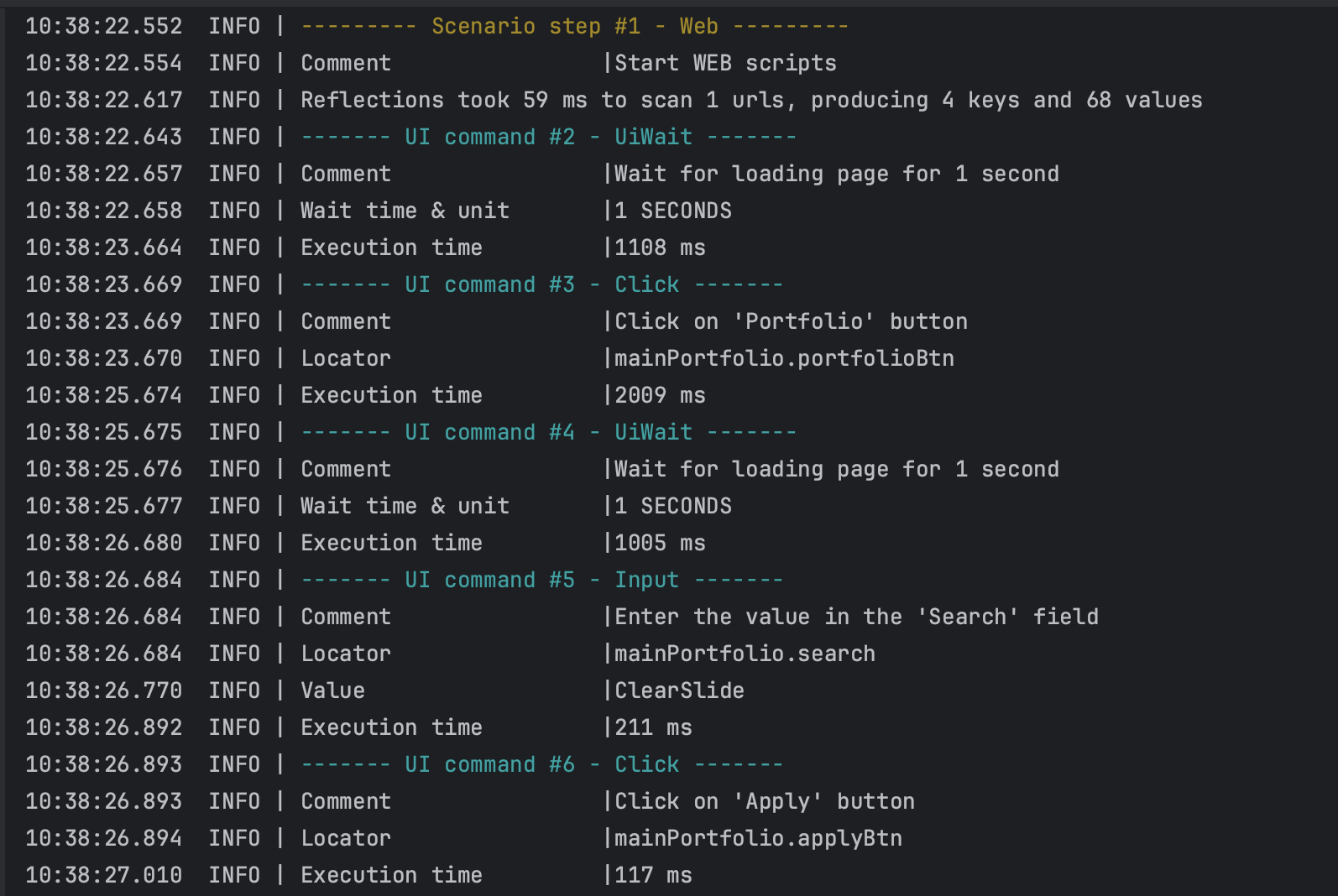
In these logs, we can see all the specific steps in passing our test scenarios, with a display of the transmitted and used data.
In the <click> command we see:
- Comment - a unique parameter for each tag that describes the action of the step.
- Locator - passed WEB interaction element, with folder name, and unique element name.
- Execution time - a unique value for each tag that prints the execution time of each command.
In the <wait> command we see:
- Comment - a unique parameter for each tag that describes the action of the step.
- wait time & unit - a time for which the scenario pauses the passage of the scenario to perform a certain function that requires a wait.
- Execution time - a unique value for each tag that prints the execution time of each command.
In the <input> command we see:
- Comment - a unique parameter for each tag that describes the action of the step.
- Locator - passed WEB interaction element, with folder name, and unique element name.
- Value - output of the passed value.
- Execution time - a unique value for each tag that prints the execution time of each command.
This structure allows you to quickly find errors in the test scenarios, and see the display of high-quality logs.
HTTP Log's Structure
An example of displaying a <http> request:

In the <http> command we see:
Comment- a unique parameter for each tag that describes the action of the step.Alias- the unique name of the API we are interacting with.Method- display of thehttpmethod used.Endpoint- used endpoint.Body- display of the transmitted request body.Status code- API response code.Execution time- a unique value for each tag that prints the execution time of each command.
DB Log's Structure
An example of displaying a <postgres> request:
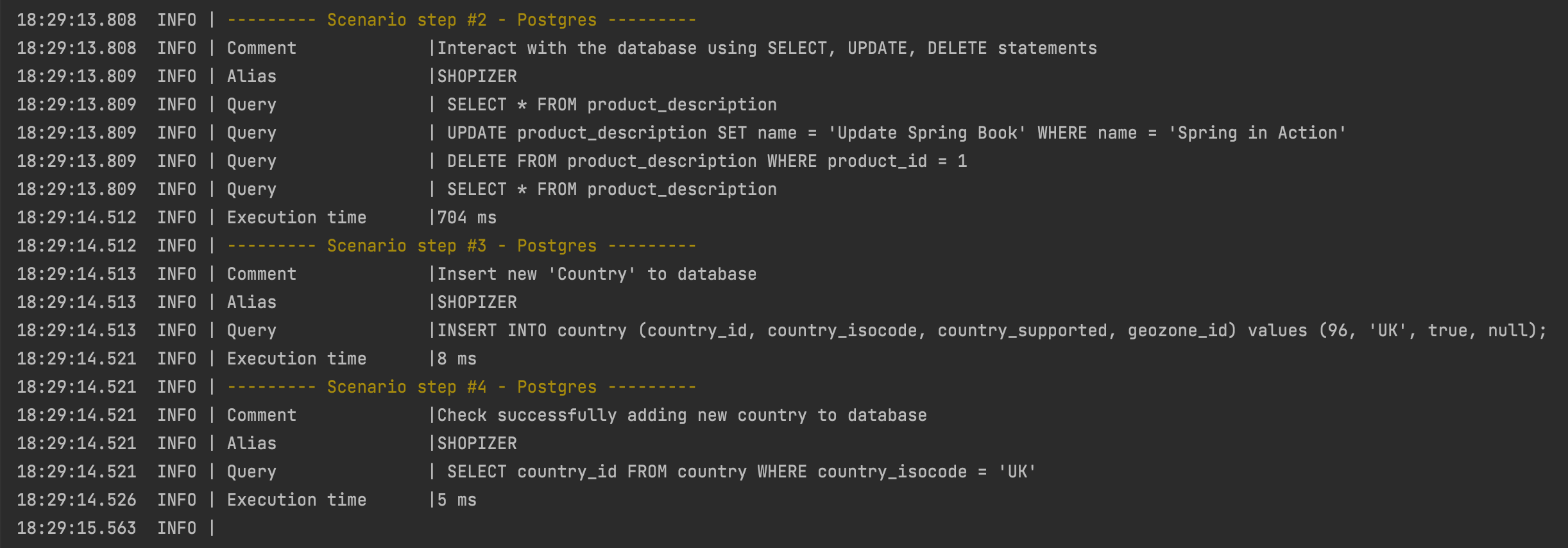
In the <postgres> command we see:
Comment- a unique parameter for each tag that describes the action of the step.Alias- unique alias of the database we are interacting with.Query- database queries.Execution time- a unique value for each tag that prints the execution time of each command.
Type to search, ESC to discard
Type to search, ESC to discard
Type to search, ESC to discard
Last updated on
Next to read:
Reporting ToolCopyright © Knubisoft
Discard Changes
Do you want to discard your current changes and overwrite with the template?
Archive Synced Block
Message
Create new Template
What is this template's title?
Delete Template
Message