Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Testing with Physical Devices
Enable USB debugging mode on your Android device
Note: enabling the developer options or debug mode on your device may differ depending on the device and OS version. In case our guide does not suit you, please check how it is done on your device’s manufacturer's official website or check the official Android Studio documentation on how it is done.
First, we need to enable developer options if they were hidden from your phone Settings until now. On your device, find the Build number option. The location of the Build number settings is usually this way: Settings > About phone > Build number (click several times).
Once developer options are enabled, we must enable the USB debugging mode on your Android device. For that, go to Settings > Additional settings > Developer Options > USB debugging and turn it on. Also, you need to enable installation via USB and USB debugging (Security settings) because devices running Android 9 (Pie) or above have restrictions on accessing certain internal settings that have been introduced.
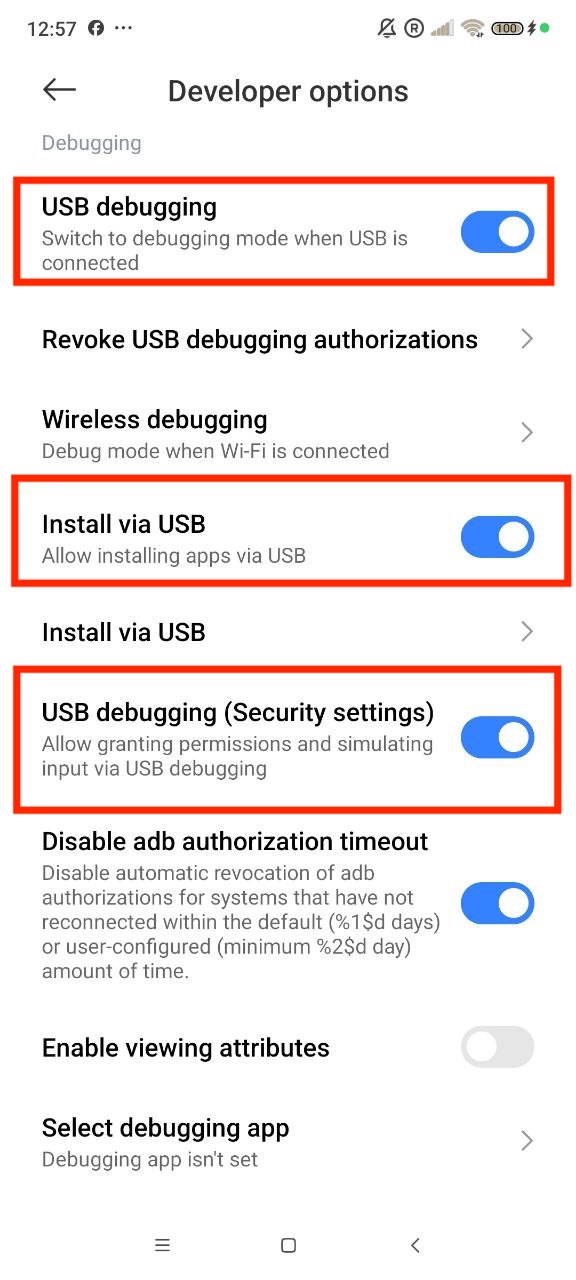
Then, connect your Android device to the computer via a USB cable and allow USB debugging mode.
Install drivers for your device
Usually, all the devices install drivers automatically once they are connected to the computer. But, if you have a problem connecting your device to your computer, try to do this:
If your device manufacturer is Google, you can install your USB drivers from Android Studio.
- Open Android Studio and go to Settings > Languages&Frameworks > Android SDK.
- In the window that opens, select the SDK Tools tab, check the box Google USB Driver, and click Apply.
For other devices:
- Find in a search engine on your computer the Device Manager settings.
- Find Portable Devices, right-click on Your Device Name, and choose Update driver.
- Choose the Search automatically option.
- Or download and install them manually from your manufacturer's official website.
Setting up the configuration file
Note: If you have not yet installed and configured Android Studio, please do it to continue with real device testing.
Open Android Studio and create a new project, then name it
Open tab View > Tool Windows > Device Manager.
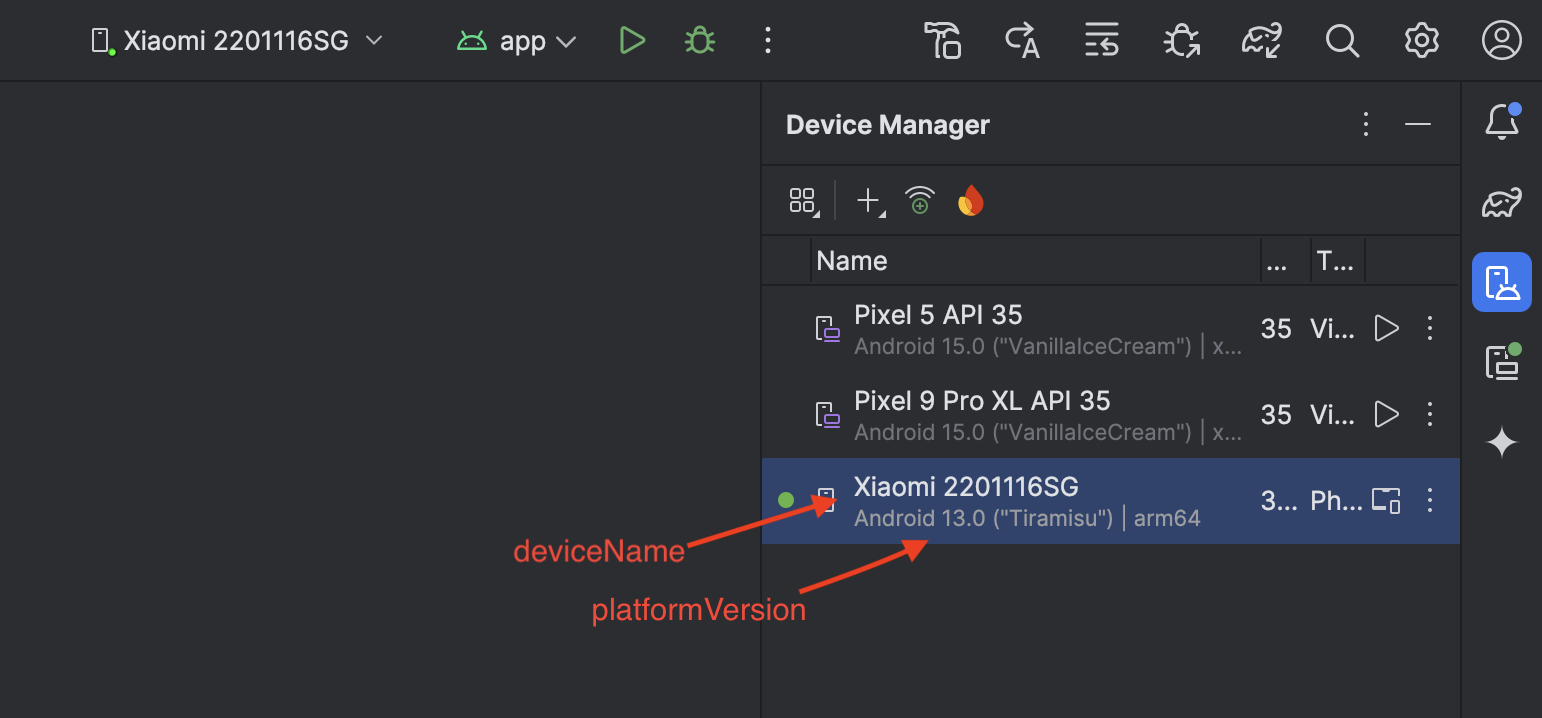
Here you’ll see your physically connected device. Now, open your 'ui.xml' file in the 'config' folder and head to the <native> block (don’t forget to choose <appiumServer> inside <connection> block and <appiumCapabilities> inside <device> block). Fill these tags:
- <deviceName> - copy your device name from Android Studio and paste it into your 'ui.xml'.
- <platformVersion> - you can find it on your device in Settings > About phone, or you can see it in the Android Studio.
- <udid> - open CLI on your computer, type command adb devices, and press enter.
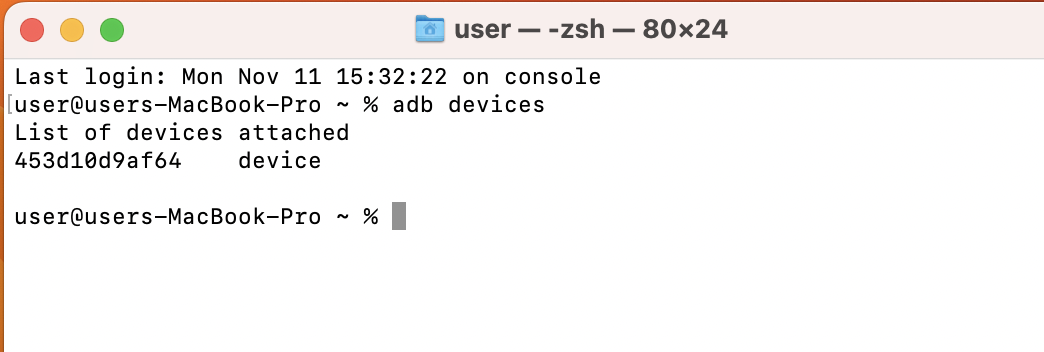
Copy/paste this ID in the tag.
The next step is launching the Appium (you should install it if you haven't it yet). You can use the command appium in the Testlum's terminal.
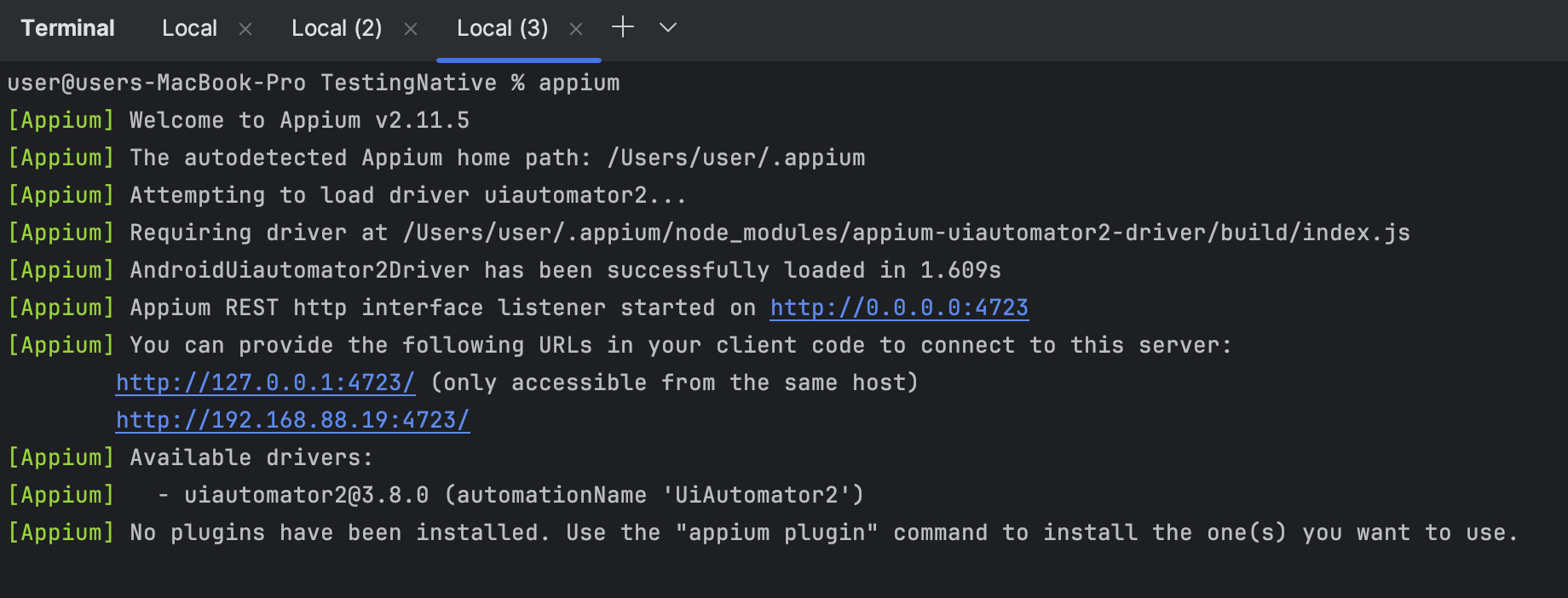
Now your config file should look like this:
<native enabled="true"> <takeScreenshots enable="false"/> <elementAutowait seconds="300"/> <connection> <appiumServer> <serverUrl>http://127.0.0.1:4723/</serverUrl> </appiumServer> </connection> <devices> <device alias="NATIVE_0" platformName="android" enabled="true"> <appiumCapabilities> <deviceName>Xiaomi 2201116SG</deviceName> <platformVersion>13.0</platformVersion> <udid>453d10d9af64</udid> <appPackage>com.todoist</appPackage> <appActivity>com.todoist.activity.HomeActivity</appActivity> </appiumCapabilities> </device> </devices></native>It remains only to fill in the <appPackage> and <appCapability> tags of the application that you are going to test.
Note that after running the test scenario in the Testlum, it can be offered by your device to install Appium Settings automatically on your physical device. You should agree to it.
Copyright © Knubisoft